Visualize AXIS Object Analytics data using Grafana® dashboard
This how-to guide shows you how to visualize data produced by a Crossline counting scenario, in AXIS Object Analytics, on a Grafana® dashboard.
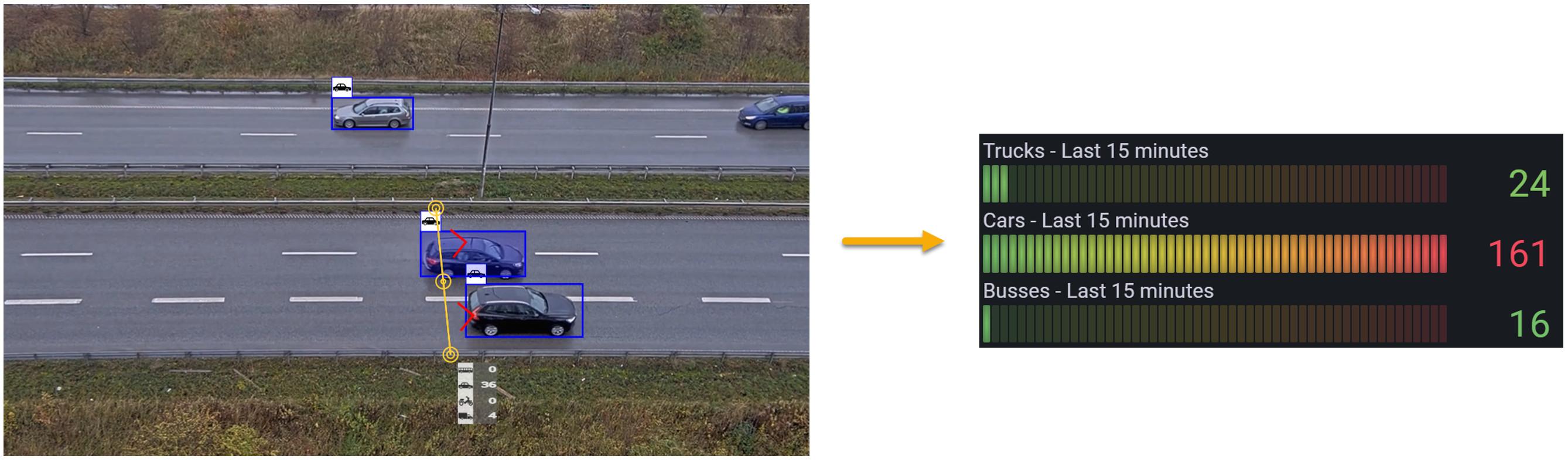
Screenshot from Grafana to the right
It uses MQTT as a secure transport protocol from the camera to AWS. AWS IoT Core (MQTT broker) receives the MQTT messages from the camera and forwards them to a time-series database (Amazon Timestream) for storage and further processing. A local or cloud instance of Grafana is connected to the Amazon Timestream database, which queries the data and displays it visually in graphs and tables.
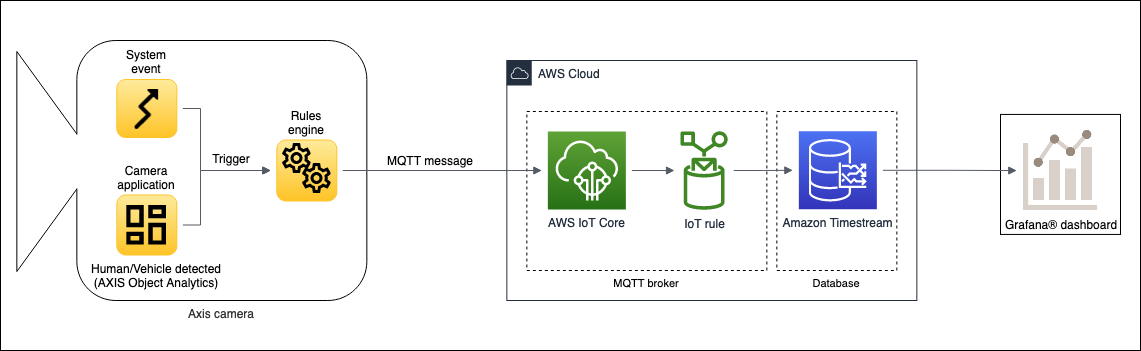
Some sections can be replaced or changed to get a solution that fits other use cases. For example, replace AXIS Object Analytics with some other analytics or triggers that send metadata to the AWS cloud. Or, replace the Grafana visualization dashboard with some other data visualization platform.
Prerequisites
- Axis camera running AXIS Object Analytics
- Access to AWS cloud services
- Local or cloud instance of Grafana
The Amazon Timestream service isn't available in all regions. For this setup to work, select one of its supported regions for all AWS services used in this how-to guide.
Click here to see AXIS Object Analytics compatible cameras.
Workflow
- Provision AWS IoT Core and Things
- Connect the camera's MQTT client to AWS IoT Core
- Configure AXIS Object Analytics to send MQTT messages
- Provision Amazon Timestream
- Route messages from AWS IoT Core to Amazon Timestream
- Verify data in Amazon Timestream
- Connect Grafana to Amazon Timestream
- Grafana dashboard examples
Provision AWS IoT Core and Things
Provisioning an AWS IoT Core service provides an MQTT broker to which the Axis camera can connect:
- Sign in to the AWS Console and search for IoT Core.
- Go to Manage > All devices > Things and click Create things.
- Select Create single thing and click Next.
- Enter a unique name and click Next.
- On the Configure device certificate page, select Auto-generate a new certificate and click Next.
- Create a new or attach an existing policy to the certificate. You're redirected to a new page if you create a new policy. For this how-to guide, create a new policy with two statements:
- First statement
- Policy effect:
Allow - Policy action:
iot:Connect - Policy resource:
*
- Policy effect:
- Second statement
- Policy effect:
Allow - Policy action:
iot:Publish - Policy resource:
*
- Policy effect:
warningNot restricting the policy resource is acceptable in an exploratory phase, but applying least-privilege permissions is a requirement before going to production.
- First statement
- Return to the previous page to attach the applicable policies and click Create thing.
- Download the Device certificate, Public key file, Private key file and the Root CA certificate.
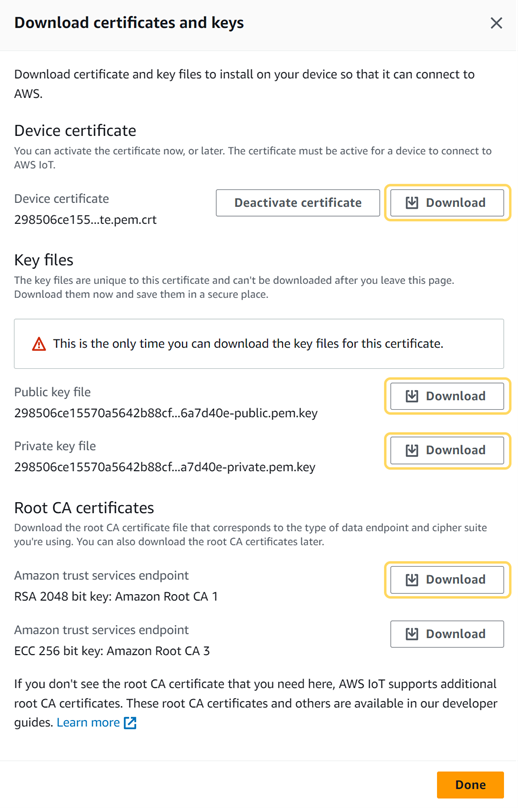
Screenshot from AWS Console - Click Done.
Connect the camera's MQTT client to AWS IoT Core
First, install the client and CA certificates on the Axis camera to enable a secure MQTT connection to the AWS IoT Core MQTT broker:
- Log in to the Axis camera and go to System > Security.
- Click Add certificate.
- Select Upload a client-server certificate using a separate private key and click Next.
- Upload the client certificate (filename ends with
certificate.pem.crt) and the private key (filename ends withprivate.pem.key), and click Next. - Click Install and then Close.
- Click Add certificate again and select Upload a CA certificate.
- Upload the root CA certificate (
AmazonRootCA1.pem). - Click Next and then Install.
Next, configure the camera's MQTT client:
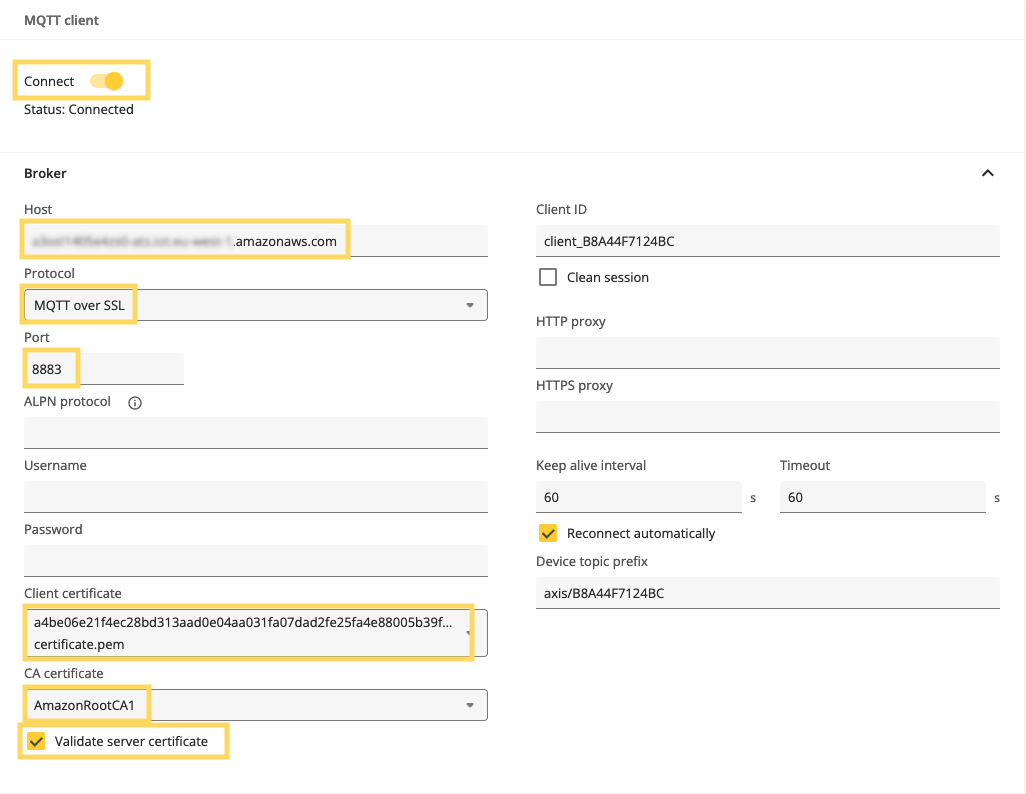
- In the web interface of Axis camera, go to System > MQTT.
- Under Host, enter the hostname for the IoT Core MQTT broker. You can find the hostname (endpoint) to the MQTT broker in the AWS Console under IoT Core > Settings.
- Under Protocol, select MQTT over SSL using default port 8883.
- Under Client certificate, select the previously uploaded client certificate.
- Under CA certificate, select the previously uploaded CA certificate.
- Select Validate server certificate.
- Click Save.
- Turn on Connect.
Here is an example of an MQTT client setup in an Axis camera.
Configure AXIS Object Analytics to send MQTT messages
- In the camera's web interface, go to Analytics > AXIS Object Analytics and click Start.
- Open AXIS Object Analytics.
- Select Crossline counting and click Next.
- Select the type of objects you are interested in, and click Next.
- Configure the virtual line and trigger direction.
- Click Finish.
With the scenario created, let's configure the MQTT client.
-
Go to System > MQTT > MQTT publication.
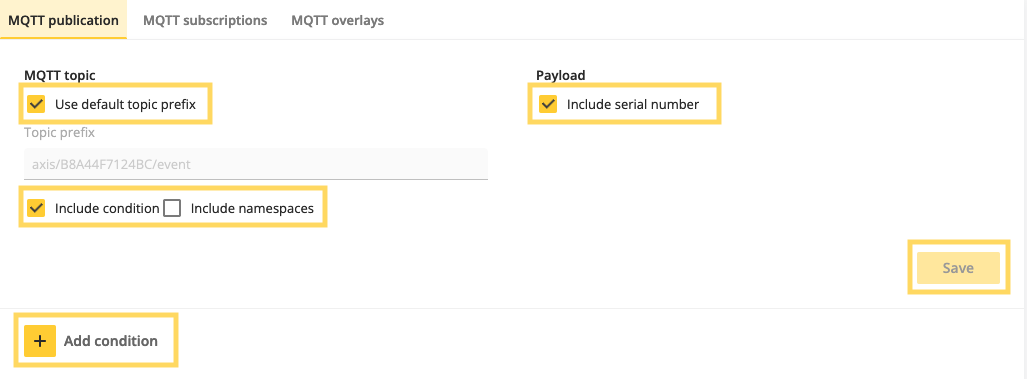
-
Select Use default topic prefix to include the serial number in the MQTT topic. Select Include serial number and Include condition. Make sure to clear Include namespaces to get an MQTT topic structure that can be handled by the AWS IoT Core rule. Click Save.
-
Click Add condition and select the scenario created earlier in AXIS Object Analytics.
-
Click Add to save the changes.
-
In the AWS Console, go to IoT Core and make sure that the MQTT communication is working.
-
Go to Test > MQTT test client.
-
Enter
#as Topic filter to see all incoming MQTT messages to the broker. -
Click Subscribe. A new MQTT message is displayed every time an object passes the line configured in AXIS Object Analytics.
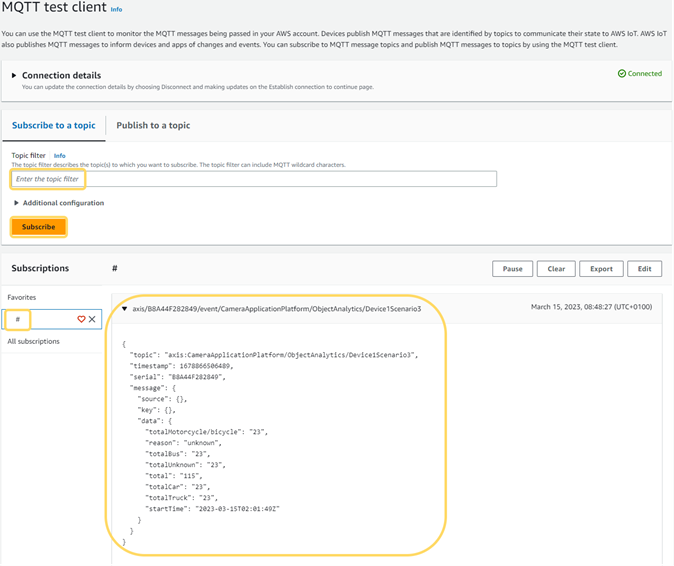
Screenshot from AWS ConsoleMQTT payload example of a message produced by a Crossline counting scenario{
"topic": "axis:CameraApplicationPlatform/ObjectAnalytics/Device1Scenario1",
"timestamp": 1670518346712,
"serial": "0123456789AB",
"message": {
"source": {},
"key": {},
"data": {
"startTime": "2022-12-06T22:01:25Z",
"reason": "car",
"total": "20960",
"totalBus": "0",
"totalCar": "18103",
"totalHuman": "0",
"totalMotorcycle/bicycle": "0",
"totalTruck": "2857",
"totalUnknown": "0"
}
}
}In case there aren’t any objects passing the line while testing, you can click Test events to manually trigger events in AXIS Object Analytics.
Provision Amazon Timestream
- In the AWS Console, search for the Amazon Timestream service.
- Click Create database.
- Select Standard database and enter a name for the database.
- Click Create database.
- Go to Tables and click Create table.
- Set a data retention time for both memory and magnetic storage. For more information See AWS documentation.
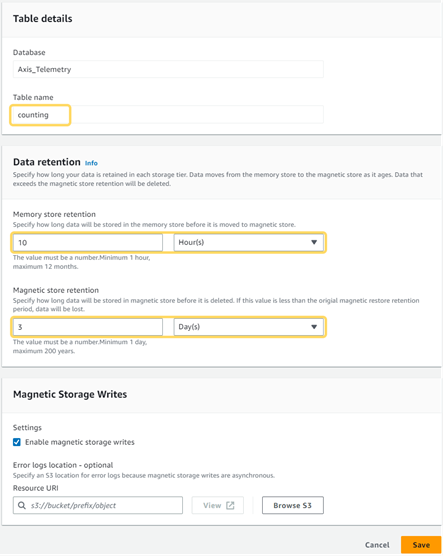
Screenshot from AWS Console
Route messages from AWS IoT Core to Amazon Timestream
-
Access IoT Core in the AWS Console.
-
Go to Manage > Message routing > Rules.
-
Click Create rule.
-
Enter a Rule name and click Next.
-
On the Configure SQL statement page, enter the following SQL query:
SQL querySELECT message.data.reason
FROM 'axis/+/event/CameraApplicationPlatform/ObjectAnalytics/#'The statement selects the
reasonmeasurement found in the MQTT payload, sent by AXIS Object Analytics using the MQTT topicaxis/0123456789AB/event/CameraApplicationPlatform/ObjectAnalytics/Device1Scenario1.Payload with reason data{
"topic": "axis:CameraApplicationPlatform/ObjectAnalytics/Device1Scenario1",
"timestamp": 1670519332535,
"serial": "0123456789AB",
"message": {
"source": {},
"key": {},
"data": {
"startTime": "2022-12-06T22:01:25Z",
"reason": "car",
"total": "21093",
"totalBus": "0",
"totalCar": "18222",
"totalHuman": "0",
"totalMotorcycle/bicycle": "0",
"totalTruck": "2871",
"totalUnknown": "0"
}
}
}infoThe MQTT topic wildcards
+and#are used in the SQL statement.+matches any character between the two slashes/+/. Use the wildcard+instead of explicitly stating the MAC address to allow all cameras to route their data to the database.#at the end of the statement matches any character, including/. This means that the statement will match any topic structure after/ObjectAnalytics/. This will allow all AXIS Object Analytics scenarios to route their data to the database.
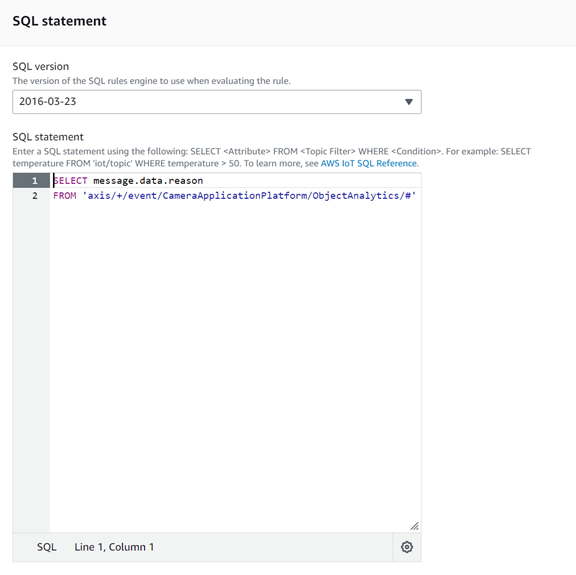
Screenshot from AWS Console -
Click Next.
-
On the Attach rule actions page, select Timestream table as Action 1.
-
Select the database and the table.
-
Enter a name in the Dimensions name field.
-
Set the Dimension value to
${serial}, which in this case represents the MAC address of the camera. -
Add a new dimension and set a Dimension name and the Dimension value to
${topic}, which in this case represents a unique scenario in the AXIS Object Analytics application. -
Under IAM role, click Create new role and enter a Role name. This automatically generates an IAM role.
infoFor the MQTT messages to be stored in the database, it is necessary to grant the IoT Core service access to the Amazon Timestream service.
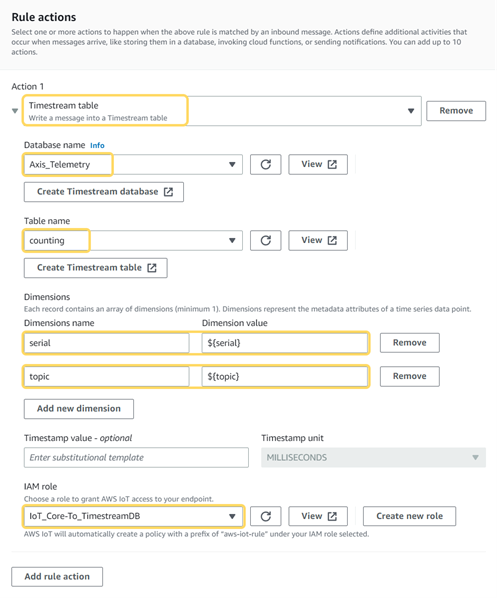
Screenshot from AWS Console -
Click Next.
-
Verify that all the information is correct and click Create.
Verify data in Amazon Timestream
-
Access Amazon Timestream in the AWS Console.
-
Go to Management Tools > Query editor.
-
Enter the following query to list the 10 most recently added data points:
SQL querySELECT *
FROM <database>.<table>
ORDER BY time DESC
LIMIT 10<database>is the name of your database and<table>is the name of your table.infoIf the name of your database or table contains special characters, you may need to encapsulate the name in quotation marks. For example, if the database is named
my-databaseand the table is namedmy-table, the table reference is"my-database"."my-table". -
Click Run to execute the query.
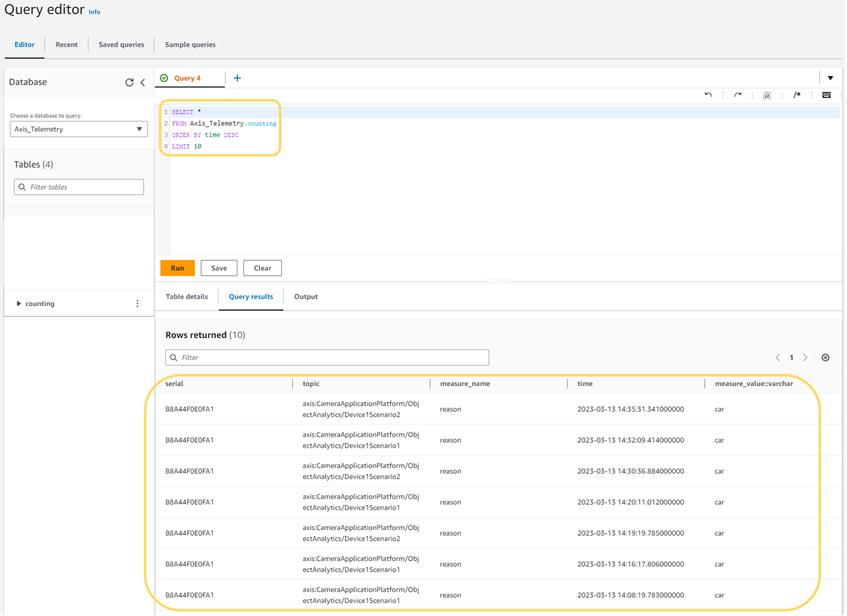
Screenshot from AWS Console
Connect Grafana to Amazon Timestream
There are several ways of provisioning a Grafana instance, depending on your domain expertise or existing environments. We won't provide you with provisioning instructions. Instead, we'll give you a few different options:
- Pull and run a self-managed Grafana Docker image
- Download and install a self-managed Grafana instance
- Provision a managed instance on Grafana Cloud
- Provision an Amazon Managed Grafana
With a running Grafana instance, complete the following steps to build a dashboard:
-
In Grafana, go to Configuration > Plugins.
-
Search for the Amazon Timestream plugin and click Install.
-
Once the plugin is installed, click Create a Amazon Timestream data source.
-
In AWS console, Access the IAM service to setup a user with the correct permissions and policy. This is done to handle the authentication from Grafana to Amazon Timestream.
-
Go to Access management > Users and click Add users.
-
Enter a name and click Next.
-
On the Set permissions page, select the Attach policies directly option and search for the AmazonTimestreamReadOnlyAccess policy name. Select it and click Next.
-
Make sure the information is correct and then click Create user.
-
Select the created user and go to the Security credentials tab.
-
Scroll down to Access keys and click Create access key.
-
Select the Third-party service option and click Next.
-
Click Create access key. Take note of the Access key and Secret access key as these credentials are required when establishing the connection from Grafana to Amazon Timestream.
-
In Grafana, select Access & secret key as Authentication Provider, and enter Access Key ID and Secret Access Key.
-
In the Default Region field, enter the region in which you created your Amazon Timestream database.
infoA region is defined by its ID, but it also has a more descriptive name. For example, the region with ID
us-east-1corresponds toNorth Virginia. If you're not sure which region to select, go to your Amazon Timestream database and in its summary in the AWS Console, and look at the Database ARN. The format of the ARN isarn:aws:timestream:<region>:<account>:database/<database>. -
With the default regions selected, you can now select Database, Table, and Measure, all of which have been configured in AWS.
-
Click Save and test to verify that the connection has been established.
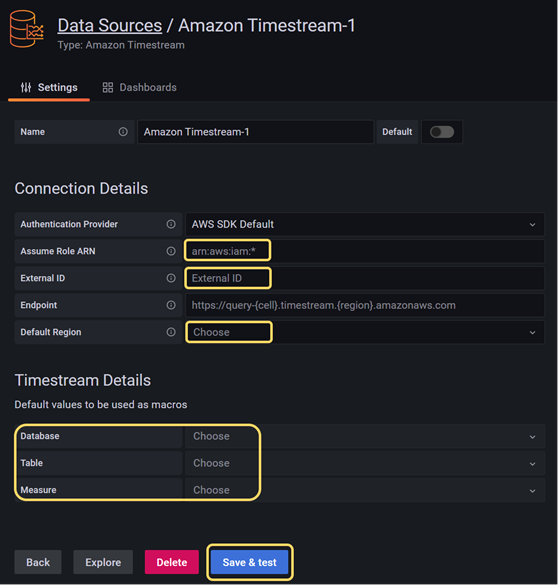
Screenshot from Grafana -
Once Grafana and Amazon Timestream are connected, click Dashboards > New Dashboard.
-
Add a new panel.
-
In the Data source field, select Amazon Timestream and then ensure that the appropriate Database, Table, and Measure values are selected.
-
Enter an SQL query to visualize the data stored in Amazon Timestream. See the examples for queries that can provide insights using graphical representations of the data.
Grafana dashboard examples
Below are some SQL queries that you can use to visualize the object counting data produced by AXIS Object Analytics.
Example 1
Count the number of cars in the time range selected for the current dashboard. Aggregated counts in 1-hour sections.
SELECT count(*) AS Cars, BIN(time, 1h) AS bin_time
FROM $__database.$__table
WHERE measure_value::varchar = 'car' AND topic = 'axis:CameraApplicationPlatform/ObjectAnalytics/Device1Scenario1' AND serial = '0123456789AB'
GROUP BY BIN(time, 1h)
ORDER BY bin_time
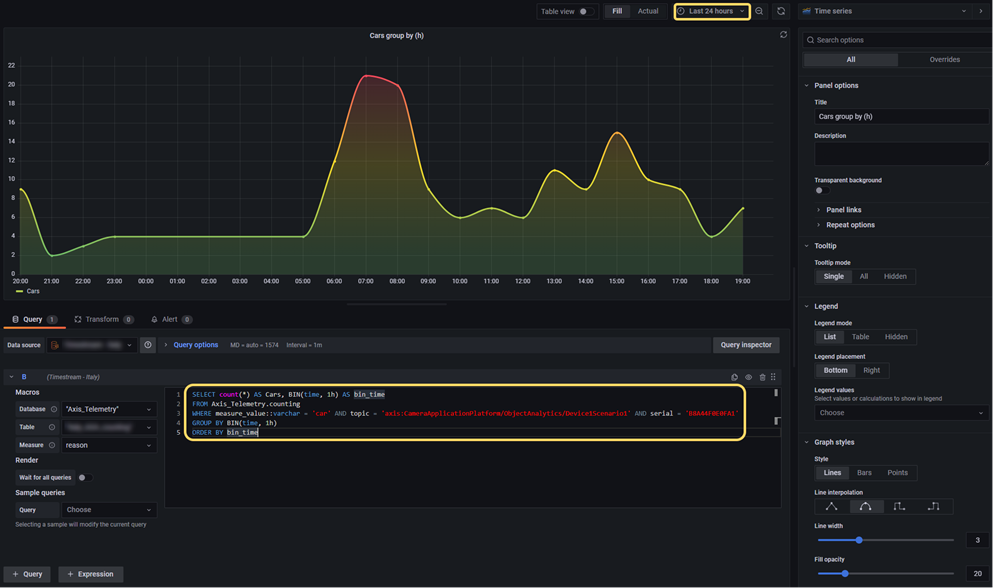
Screenshot from Grafana
Example 2
Count the number of cars in fixed time ranges such as the last hour, the last day, or the 7 days.
SELECT count(*) AS "Last hour"
FROM $__database.$__table
WHERE measure_value::varchar = 'car' AND time between ago(1h) and now() AND topic = 'axis:CameraApplicationPlatform/ObjectAnalytics/Device1Scenario1' AND serial = '0123456789AB'
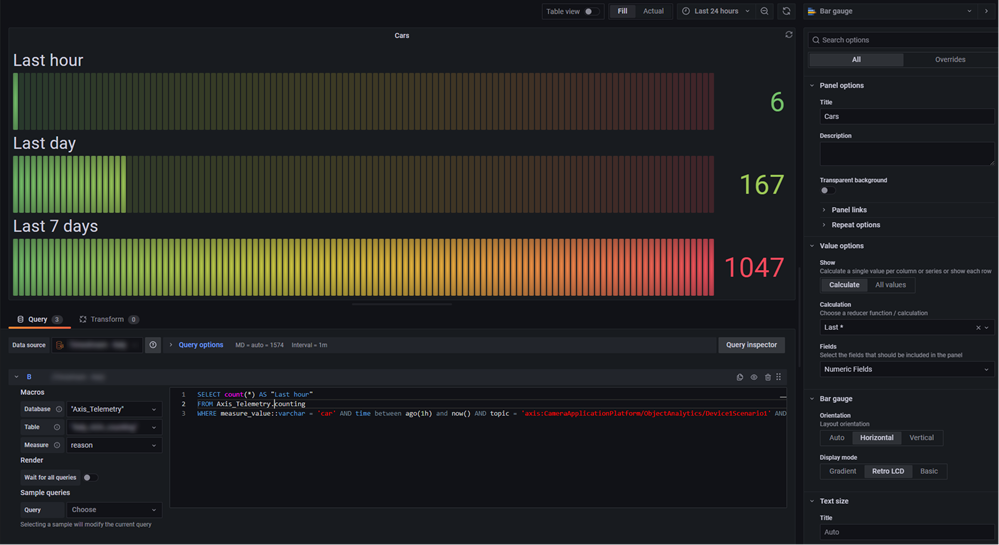
Screenshot from Grafana
Inspirational dashboard
The following dashboard shows different panels that represent several object detections by AXIS Object Analytics. E.g. Humans, Cars, and Motorcycles/Bicycles in defined directions.
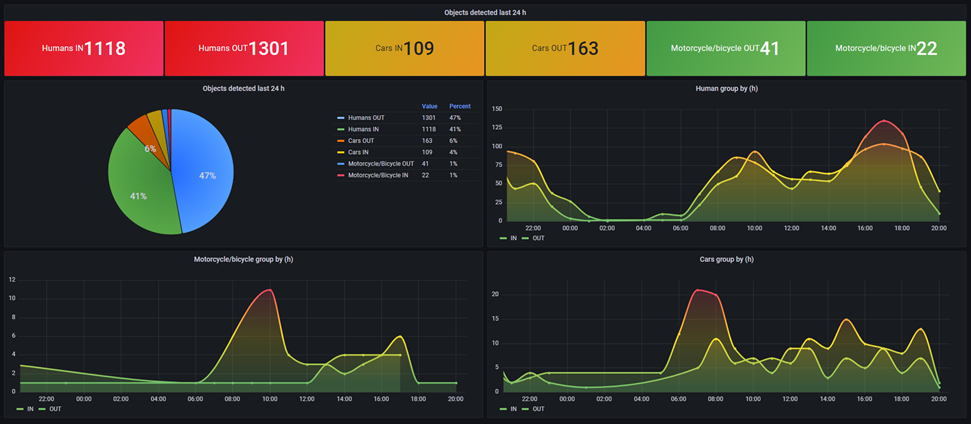
Screenshot from Grafana
Disclaimer
The Grafana Labs Marks are trademarks of Grafana Labs, and are used with Grafana Labs’ permission. We are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by Grafana Labs or its affiliates. Amazon Web Services, AWS and the Powered by AWS logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. Docker and the Docker logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Docker, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. Docker, Inc. and other parties may also have trademark rights in other terms used herein. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners, and we are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by them or their affiliates.
As described in this document, you may be able to connect to, access and use third party products, web sites, example code, software or services (“Third Party Services”). You acknowledge that any such connection and access to such Third Party Services are made available to you for convenience only. Axis does not endorse any Third Party Services, nor does Axis make any representations or provide any warranties whatsoever with respect to any Third Party Services, and Axis specifically disclaims any liability or obligations with regard to Third Party Services. The Third Party Services are provided to you in accordance with their respective terms and conditions, and you alone are responsible for ensuring that you (a) procure appropriate rights to access and use any such Third Party Services and (b) comply with the terms and conditions applicable to its use.
PLEASE BE ADVISED THAT THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, AND IS NOT INTENDED TO, AND SHALL NOT, CREATE ANY LEGAL OBLIGATION FOR AXIS COMMUNICATIONS AB AND/OR ANY OF ITS AFFILIATES. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE USE, RESULTS AND PERFORMANCE OF THIS DOCUMENT AND ANY THIRD PARTY SERVICES REFERENCED HEREIN IS ASSUMED BY THE USER OF THE DOCUMENT AND AXIS DISCLAIMS AND EXCLUDES, TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, ALL WARRANTIES, WHETHER STATUTORY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, TITLE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT AND PRODUCT LIABILITY.